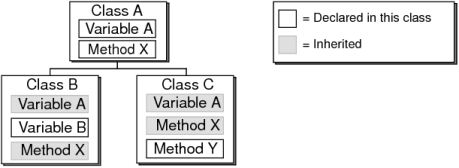
A mechanism whereby one class of objects can be defined as a special case of a more general class and includes the method and variable definitions of the general class, known as a base or superclass. The superclass serves as the baseline for the appearance and behavior of the descendant class, which is also known as a subclass. In the subclass, the appearance, behavior, and structure can be customized without affecting the superclass. Figure G-28 shows an example of inheritance.
|
Figure G-28
|