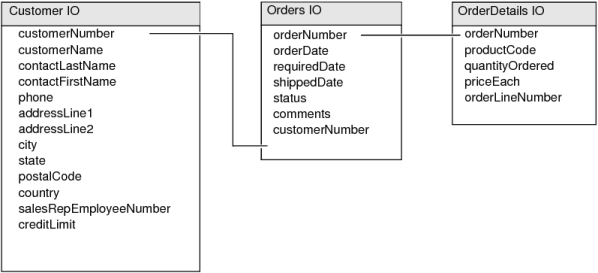
You can retrieve data from any number of information objects as long as there is a relationship, identified by common fields, among the information objects. Figure 11-1 shows three information objects and the fields that join them. The Customer IO is joined to the Orders IO through the customerNumber field, and the Orders IO is joined to the OrderDetails IO through the orderNumber field.
|
1
|
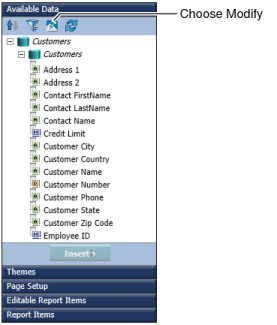
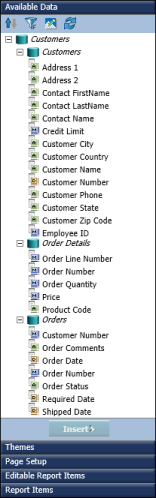
Under Available Data, choose Modify, as shown in Figure 11-2. This figure also shows an example of Available Data displaying the data fields in the first information object, Customers.
|
|
Figure 11-2
|
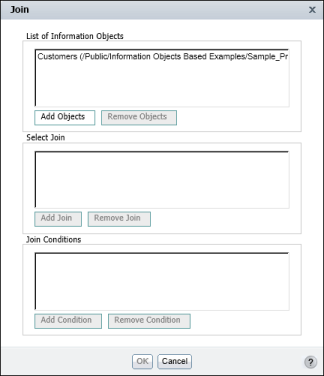
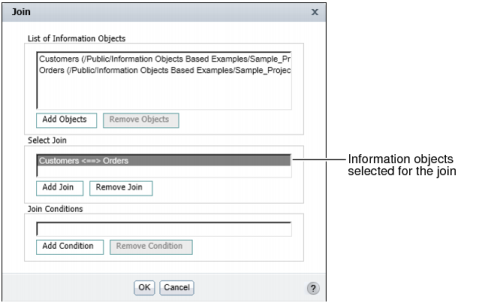
Join displays the information object, Customers, under List of Information Objects, as shown in Figure 11-3.
|
2
|
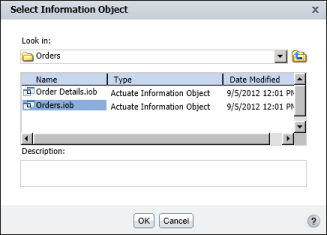
On Select Information Object, browse through the folders to find and select an information object. Figure 11-4 shows an example of Select Information Object displaying the contents of a folder, which includes two information objects.
|
|
2
|
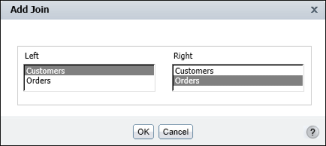
In Left, select one information object. Then, in Right, select the other information object. Figure 11-5 shows an example where CustomerData and OrderData are selected in the Left and Right fields, respectively.
|
|
3
|
|
3
|
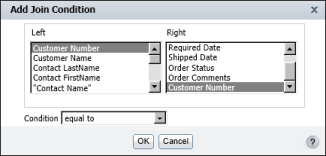
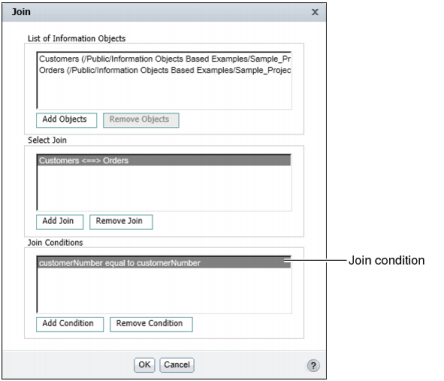
In Condition, select a comparison operator. Typically, you use the default operator, equal to. Figure 11-7 shows an example of a completed join condition. The join condition joins the information objects on their respective customerNumber fields. This condition retrieves only those rows in which the customerNumber values match.
|
|
Figure 11-7
|
|
Figure 11-8
|
Available Data displays all the data fields from the joined information objects that you can insert in a table in your report design. In Figure 11-9, Available Data shows the data fields in three information objects, CustomerData, OrderData, and OrderDetailsData.