How to create a computed measure using a relative time period calculation
1 Choose New Computed Measure.
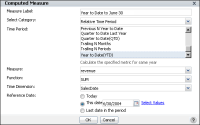
2 In Computed Measure, complete the following tasks, as shown in
Figure 4‑19. These tasks differ depending on the category and time period you select.
Figure 4‑19 Creating a year-to-date computed measure

In Measure Label, type a name for the new measure. The name you specify appears in the heading.

In Select Category, select Relative Time Period.

In Time Period, select a time period from the list. For example, select Year to Date.

In Measure, select a measure to which to apply the function. For example, select revenue.

In Function, select one of the following functions to apply to the measure:

AVERAGE

COUNT

MAX

MIN

SUM
For example, select SUM to display the sum values for each year.

In Time Dimension, select a dimension to which to apply the function.

In Reference Date, select one of the following options:

To use today’s date as the reference date, select Today.

To specify a date, select This date. Then, type a date or choose Select Values to display the calendar tool from which you select a date. For example, select This date and type 06/30/2004.

To specify the last date in the available time period, select Last date in the period.
Choose OK.
The cross tab displays the computed measure values, as shown in
Figure 4‑20.
Figure 4‑20 Displaying the Year-to-Date to June 30 computed measure
Using the * to Date and Trailing N * time periods
Data Analyzer calculates time periods, such as Month to Date, Month to Date Last Year, Quarter to Date, Quarter to Date Last Year, Previous Month to Date, Previous N Year to Date, Next N Periods, and Trailing N Periods, using the year, month, and day parts of a reference date. For example, Month to Date covers the period starting at the beginning of the reference date’s month and ending at the reference date. If the reference date is 2012-01-08, the period is 2012‑01-01 to 2012‑01-08. Contrast this with Current Month, which is calculated using only the year and month parts of a reference date. For a reference date of 2012-01-08, Current Month covers the entire month, 2012-01-01 to 2012-01-31.
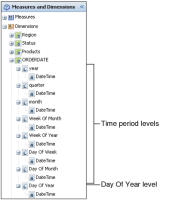
Because the * to Date and Trailing N * time periods use the day part of a reference date, the time dimension defined in the cube must include the Day Of Year level.
Figure 4‑21 shows a cross tab data pane displaying time period levels, including the Day Of Year level.
Figure 4‑21 Displaying time period levels in the data pane
If the time dimension in the cube does not include the Day Of Year level, and you use a * to Date or a Next N * or Trailing N * time period in a relative time period calculation, the measures display the wrong results. Month to Date returns the same results as Current Month, Quarter to Date returns the same results as Current Quarter, and so on. In other words, the day part of the reference date has no effect.