Specifying a condition
The condition in a conditional formatting rule is an If expression that must evaluate to True. For example:
If the order total is less than 1000
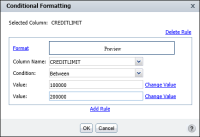
If the customer credit limit is between 100000 and 200000
If the sales office is Tokyo
If the order date is 7/21/2008
The Conditional Formatting dialog box helps you construct the If expression by breaking it down into its logical parts. In
Figure 3‑6, the expression consists of three parts. In
Figure 3‑9, the expression has four parts.
In Column Name, select a column. This column contains the value that determines when conditional formatting takes effect. The column you select here does not have to be the same as the column that you selected for formatting in the report. For example, if Product Name is the column selected for formatting, you can select Profit in this field to indicate that for a certain profit amount, conditional formatting applies to the product name.
Figure 3‑9 Selecting data fields between two values
In Condition, select the comparison test, or operator, to apply to the column you selected. You can select Equal to, Less than, Less than or Equal to, and so on. If you select Is Null, Is Not Null, Is True, or Is False, the If expression does not require additional information.
If you select an operator that requires a comparison to one or more values, one or more additional fields appear. For example, if you select Less than or Equal to, a third field appears. In this field, type the comparison value. If you select Between or Not Between, a third and fourth field appear. In these fields, type the lower and upper values, respectively, as shown in
Figure 3‑9.