Data types
One of the fundamental concepts to understand is data types. Data types are the types of values—numbers, strings, and Booleans, for example—that can be represented and manipulated in any programming language. Every database field has a certain data type, every piece of report data has a certain data type, and every expression you create returns a value of a particular data type.
This concept is important because if an expression does not handle data types properly, errors occur or the report returns unexpected results. For example, you cannot perform mathematical calculations on numbers if they are of string type, and you cannot convert values in a date field to uppercase characters.
If writing an expression to manipulate a data set field, verify its type, particularly if the field values are numbers. Numbers can be of string or numeric type. For example, databases typically store zip codes and telephone numbers as strings. Item quantities or prices are always of numeric type so that the data can be manipulated mathematically. IDs, such as customer IDs or order IDs are usually of numeric type so that the data can be sorted in numeric order, such as 1, 2, 3, 10, 11, rather than in alphanumeric order, such as 1, 10, 11, 2, 3.
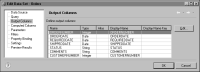
To see the data type of a field, open the data set in Data Explorer, and choose Output Columns. Output Columns displays the fields in the data set and their types, as shown in
Figure 11‑1.
Figure 11‑1 Output Columns